認知・情動脳科学専攻 Major of Cognitive and Emotional Neuroscience
Molecular neurobiological study of higher brain functions
 分子神経科学 Molecular Neuroscience
分子神経科学 Molecular Neuroscience森 寿 Hisashi Mori
- TEL : 076-434-7230
- URL : http://www.med.u-toyama.ac.jp/molneurosci/index.html
- Keywords : Glutamate receptor, Gene targeting, Neuroimaging, Neuroimmunology
研究の背景と目的 Background and Purpose of Study
脳神経機能と病態の分子基盤を明らかにすることは、病態の新たな診断マーカーや創薬標的の同定につながります。これまで、様々な脳機能に重要なグルタミン酸神経伝達の個体での機能を、遺伝子ノックアウトマウスを作製し解析してきました。また、NMDA型グルタミン酸受容体の機能制御に関わるD-セリンの合成酵素(SRR)を標的とした創薬研究を、生命融合科学教育部の研究者と共同で進めています。さらに、ストレスによる記憶学習制御機構解析、生体発光を用いた新たなイメージング技術の開発などの研究も進めています。
We have focused on the molecular basis of brain functions and dysfunctions. We examined the functions of diverse glutamate receptor (GluR) channels with the generation and analysis of the gene targeting mice. We revealed that the diverse GluR channels play important roles in the formation of neural network, synaptic plasticity, learning and memory, and neuropathological disorders. Now, we try to develop novel compounds targeting serine racemase, the enzyme producing NMDA-type GluR coagonist D-serine, in collaboration with the members of the Graduate School of Innovative Life Science. Furthermore, we are investigating the molecular mechanism of stress-modulated learning and memory and developing novel in vivo bioluminescent imaging to detect brain functions and dysfunctions.
本研究の領域横断性
我々の研究分野では、分子遺伝学的手法を用いて研究を進めており、遺伝子や分子の機能を、試験管レベル、細胞レベル、個体レベルで解析する遺伝子操作実験が可能です。また、遺伝子操作マウスを病態モデルとして評価し、薬物効果の判定等により、新たな創薬標的の同定等の共同研究も可能です。
研究内容
1)遺伝子ノックアウトマウスを用いた認知・情動・社会性の分子機構解析
前頭前野、扁桃体、視床など認知・情動の中心となる脳部位特異的遺伝子操作マウスを作製し、神経伝達とストレスホルモン等による脳機能制御に注目して個体レベルで行動学的解析を行い、認知・情動過程と発達に与える影響を解析しています(図1)。また、行動変化の基盤となっている遺伝子発現、蛋白質修飾等を解析しています。さらに、遺伝子操作マウスを病態モデルマウスとして評価し、精神・神経疾患の治療に道を拓く研究を行っています。
図1:扁桃体亜核選択的な遺伝子ノックアウトマウス
(脳冠状断面、遺伝子欠損が起きた脳部位がlacZ染色される)
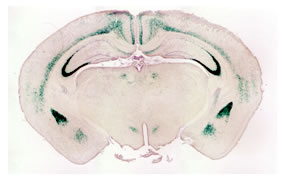
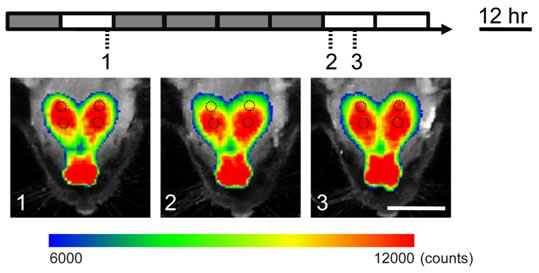
図2:視覚入力依存的な脳内遺伝子発現イメージングマウス(発光の疑似カラー表示)
これらの新たな遺伝子操作マウス作製のために、マウスゲノム遺伝子を大腸菌内で操作する技術開発や、コンディショナルノックアウトを行うための遺伝子組み換え酵素の改良なども進めています。遺伝子ノックアウトマウス解析の研究成果として、NMDA型 GluR 機能を制御するD-セリンが、神経細胞に発現するセリンラセマーゼにより産生され、様々な脳機能や脳病態に関わることを明らかにし、セリンラセマーゼを標的とした創薬研究を進めています(文献1-3)
2)生体マウス脳内での分子イメージング法の開発と解析
遺伝子発現、タンパク質相互作用、細胞内シグナル伝達などの脳機能における役割を、生きたマウスで計測する技術開発を行っています。例えば、神経活動依存的に発現制御されるArc遺伝子発現を、生体発光技術を用いて解析する事に成功しました(図2, 参考文献4, 5)。このマウスでは、視覚野における神経活動依存的な脳神経回路の可塑的変化や、様々な薬物効果等を生きたままのマウス個体で連続的に評価する事が可能です。 また、細胞骨格動態やタンパク質リン酸化過程におけるタンパク質間相互作用を検出する新たな発光プローブの開発を行っており、生細胞内でこれらの現象を検出する事を可能としました(参考文献6)。これらの研究によって、脳機能制御に関わるタンパク質の挙動を個体レベルで解析する事が可能となり、脳機能や脳病態の解析に応用する研究を進めています。
参考文献
- Mori H. Overview of the NMDA receptor. The NMDA Receptor (Hashimoto K. ed). The Receptor. Vol. 30. Humana Press, 2017, p1-18.
- Inoue R. and Mori, H. Serine racemase knockout mice: Neurotoxicity, Epilepsy, and Schizophrenia. D-Amino Acids physiology, Metabolism, and Application. (Yoshimura et al. eds.) Springer 2016, p119-136.
- Mori, H., Wada, R., Takahara, S., Horino, Y., Izumi, H., Ishimoto, I., Yoshida, T., Mizuguchi, M., Obita, T., Gouda, H., Hirono, S., Toyooka, N. A novel serine racemase inhibitor suppresses neuronal over-activation in vivo. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 25: 3736-3745, 2017.
- Izumi, H., Ishimoto, T., Yamamoto, H., Nishijo, H., Mori, H. Bioluminescence imaging of Arc expression enables detection of activity-dependent and plastic changes in the visual cortex of adult mice. Brain Struct. Funct., 216:91-104, 2011.
- Izumi, H., Ishimoto, T., Yamamoto, H., Mori H. Application of hairless mouse strain to bioluminescence imaging of Arc expression in mouse brain. BMC Neuroscience. (2017) 18:18.
- Ishimoto, T., Mano, H., Mori, H. In vivo imaging of CREB phosphorylation in awake-mouse brain. Sci. Rep., 5:9757, 2015.

